… (#67776)"
This detects issues in `scudo`. Reverting until these are fixed.
```
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd.h:74:12: error: returning variable 'QuarantineCache' by reference requires holding mutex 'Mutex' exclusively [-Werror,-Wthread-safety-reference]
74 | return QuarantineCache;
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/combined.h:248:28: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::TSD<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>::getQuarantineCache' requested here
248 | Quarantine.drain(&TSD->getQuarantineCache(),
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd.h:57:15: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>::commitBack' requested here
57 | Instance->commitBack(this);
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd_exclusive.h:172:27: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::TSD<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>::commitBack' requested here
172 | TSDRegistryT::ThreadTSD.commitBack(Instance);
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd_exclusive.h:33:46: note: in instantiation of function template specialization 'scudo::teardownThread<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>' requested here
33 | CHECK_EQ(pthread_key_create(&PThreadKey, teardownThread<Allocator>), 0);
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd_exclusive.h:42:5: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::TSDRegistryExT<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>::init' requested here
42 | init(Instance); // Sets Initialized.
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd_exclusive.h:130:5: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::TSDRegistryExT<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>::initOnceMaybe' requested here
130 | initOnceMaybe(Instance);
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/tsd_exclusive.h:74:5: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::TSDRegistryExT<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>::initThread' requested here
74 | initThread(Instance, MinimalInit);
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/combined.h:221:17: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::TSDRegistryExT<scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>>::initThreadMaybe' requested here
221 | TSDRegistry.initThreadMaybe(this, MinimalInit);
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/combined.h:790:5: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>::initThreadMaybe' requested here
790 | initThreadMaybe();
| ^
/b/sanitizer-x86_64-linux-autoconf/build/llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/scudo/standalone/wrappers_c.inc:36:25: note: in instantiation of member function 'scudo::Allocator<scudo::DefaultConfig, &malloc_postinit>::canReturnNull' requested here
36 | if (SCUDO_ALLOCATOR.canReturnNull()) {
```
This reverts commit 6dd96d6e80e9b3679a6161c590c60e0e99549b89.
...of guarded variables, when the function is not marked as requiring
locks:
```
class Return {
Mutex mu;
Foo foo GUARDED_BY(mu);
Foo &returns_ref_locked() {
MutexLock lock(&mu);
return foo; // BAD
}
Foo &returns_ref_locks_required() SHARED_LOCKS_REQUIRED(mu) {
return foo; // OK
}
};
```
Review on Phabricator: https://reviews.llvm.org/D153131
- On non-selected tabs, set cursor to 'pointer' to indicate they're
clickable
- Selected tab shares the same background as the contents to emphasize
that it's
associated with that content. (Compare with Google Chrome or VS Code,
which do
this similarly.)
- Hovered-over tab becomes slightly brighter to indicate that clicking
it will
make it even brighter (again, Chrome does this in a similar way).
Example:

(Mouse cursor is over "Iteration 2", but unfortunately I couldn't get
the screenshot to include the cursor.)
The assertion fails on the test
TransferTest.EvaluateBlockWithUnreachablePreds
(which I think, ironically, was introuced in the same patch as the
assertion).
This just wasn't obvious because the assertion is inside an `LLVM_DEBUG`
block
and is thus only executed if the command-line flag `-debug` is passed.
We don't
have any CI builds that do this, so it's almost guaranteed that
assertions like
this will start failing over time (if they ever passed in the first
place --
which I'm not sure about here).
It's not clear to me whether there's _some_ assertion we might be able
to make
here -- I've looked at this for a while but haven't been able to come up
with
anything obvious. For the time being, I think it's best to simply delete
the
assertion.
`LLVM_DEBUG` blocks are only run if the `-debug` command line flag is
passed.
We don't do this in any of our CI builds, so the assertion has limited
value and
it's likely it will start failing over time.
And simplify formulas containing true/false
It's unclear to me how useful this is, it does make formulas more
conveniently self-contained now (we can usefully print them without
carrying around the "true/false" labels)
(while here, simplify !!X to X, too)
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D153485
My immediate use for this is not in checked-in code, but rather the
ability to plug printed flow conditions (from analysis logs) back into
sat solver unittests to reproduce slowness.
It does allow simplifying some of the existing solver tests, though.
- Use Strategy to determine whether to fix a parameter
- Fix the `Strategy` construction so that only variables on the graph
are assigned the `std::span` strategy
Reviewed by: t-rasmud (Rashmi Mudduluru), NoQ (Artem Dergachev)
Differential revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D157441
For a function `F` whose parameters need to be fixed, we group fix-its
of F's parameters together so that either all of the parameters get
fixed or none of them gets fixed.
Reviewed by: NoQ (Artem Dergachev), t-rasmud (Rashmi Mudduluru), jkorous (Jan Korous)
Differential revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D153059
Previously, post-visit state changes were indistinguishable from
ordinary
iterations, which could give a confusing picture of how many iterations
a block
needs to converge.
Now, post-visit state changes are marked with "post-visit" instead of an
iteration number:
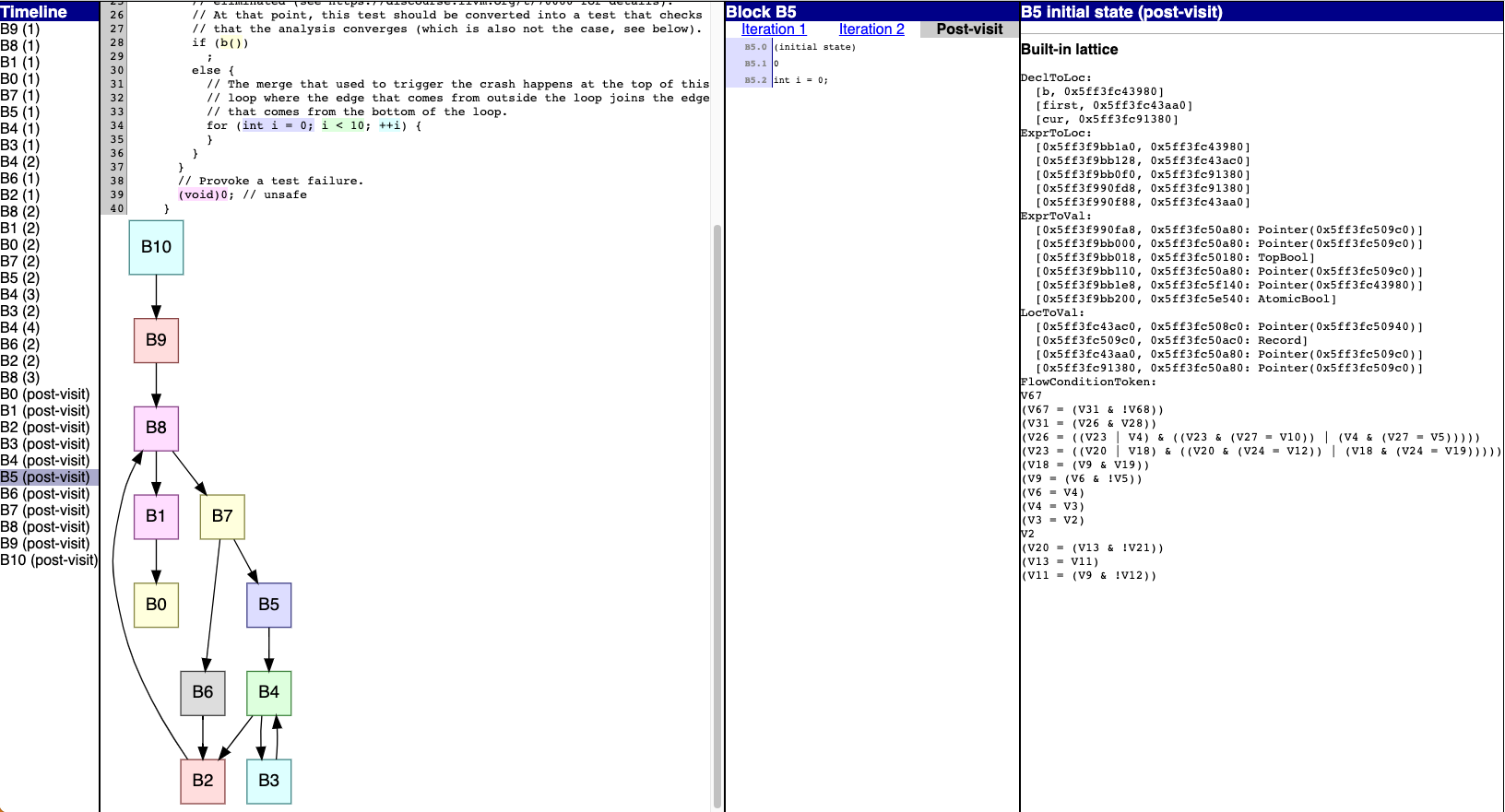)
I've received a report of a null pointer dereference happening on the
`LocDst->getType()` dereference. I wasn't unfortunately able to find a
repro,
but I'd argue the new version is better for the reduced indentation
alone.
So that the values that are accessed via such accessors can be analyzed
as a limited version of context-sensitive analysis. We can potentially
do this only when some option is set, but doing additional modeling like
this won't be expensive and intrusive, so we do it by default for now.
In C++ it seems it is legit to use base class's operator (e.g. `using
Base::operator=`) to perform copy if the base class is the common
ancestor of the source and destination object. In such a case we
shouldn't try to access fields beyond that of the base class, however
such a case seems to be very rare (typical code would implement a copy
constructor instead), and could add complexities, so in this patch we
simply bail if the method operator's parent class is different from the
type of the destination object that this framework recognizes.
This records facts that are not sensitive to the current flow condition,
and should apply to all environments.
The motivating case is recording information about where a Value
originated, such as nullability:
- we may see the same Value for multiple expressions (e.g. reads of the
same field) in multiple environments (multiple blocks or iterations)
- we want to record information only when we first see the Value
(e.g. Nullability annotations on fields only add information if we
don't know where the value came from)
- this information should be expressible as a SAT condition
- we must add this SAT condition to every environment where the
Value may appear
We solve this by recording the information in the global condition.
This doesn't seem particularly elegant, but solves the problem and is
a fairly small and natural extension of the Environment.
Alternatives considered:
- store the constraint directly as a property on the Value.
But it's more composable for such properties to always be variables
(AtomicBoolValue), and constrain them with SAT conditions.
- add a hook whenever values are created, giving the analysis the
chance to populate them.
However the framework relies on/provides the ability to construct
values in arbitrary places without providing the context such a hook
would need, this would be a very invasive change.
The template is agnostic as to the type used by the list, as long as it
is
compatible with `llvm::move` and `std::back_inserter`. In practice,
we've
encountered analyses which use different types (`llvm::SmallVector` vs
`std::vector`), so it seems preferable to leave this open to the caller.
We can dump the same information from RecordStorageLocation.
Tested the behavior before and after patch, that generates the field
values in the HTML
in both cases (and also made sure that removing the relevant code makes
the field values
in the HTML go away)
Now that prvalue expressions map directly to values (see
https://reviews.llvm.org/D158977), it's no longer guaranteed that
`RecordValue`s
associated with the same expression will always have the same storage
location.
In other words, D158977 invalidated the assertion in
`mergeDistinctValues()`.
The newly added test causes this assertion to fail without the other
changes in
the patch.
This patch fixes the issue. However, the real fix will be to eliminate
the
`StorageLocation` from `RecordValue` entirely.
I'm not sure why we had this originally, but the function seems to have
a pretty
onerous contract anyway for a function that is externally available, so
it seems
better not to keep it around.
This reapplies ddbcc10b9e26b18f6a70e23d0611b9da75ffa52f, except for a tiny part that was reverted separately: 65331da0032ab4253a4bc0ddcb2da67664bd86a9. That will be reapplied later on, since it turned out to be more involved.
This commit is enabled by 5523fefb01c282c4cbcaf6314a9aaf658c6c145f and f0f548a65a215c450d956dbcedb03656449705b9, specifically the part that makes 'clang-tidy/checkers/misc/header-include-cycle.cpp' separator agnostic.
When we call `getEnvironment`, `BlockToState[BlockId]` for the block can
return null even if CFCtx.isBlockReachable(B) returns true if it is
called from a particular block that is marked unreachable to the block.
This change makes widening act the same as equivalence checking. When the
analysis does not provide an answer regarding the equivalence of two distinct
values, the framework treats them as equivalent. This is an unsound choice that
enables convergence.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D159355
Usually RecordValues for record objects (e.g. struct) are initialized with
`Environment::createValue()` which internally calls `getObjectFields()` to
collects all fields from the current and base classes, and then filter them
with `ModeledValues` via `DACtx::getModeledFields()` so that the fields that
are actually referenced are modeled.
The consistent set of fields should be initialized when a record is initialized
with an initializer list (InitListExpr), however the existing code's behavior
was different.
Before this patch:
* When a struct is initialized with InitListExpr, its fields are
initialized based on what is returned by `getFieldsForInitListExpr()`, which
only collects the direct fields in the current class, but not from the base
classes. Moreover, if the base classes have their own InitListExpr, values
that are initialized by their InitListExpr's weren't merged into the
child objects.
After this patch:
* When a struct is initialized with InitListExpr, it collects and merges the
fields in the base classes that were initialized by their InitListExpr's.
The code also asserts that the consistent set of fields are initialized
with the ModeledFields.
Reviewed By: mboehme
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D159284
This commit replaces some calls to the deprecated `FileEntry::getName()` with `FileEntryRef::getName()` by swapping current usages of `SourceManager::getFileEntryForID()` with `SourceManager::getFileEntryRefForID()`. This lowers the number of usages of the deprecated `FileEntry::getName()` from 95 to 50.
The goal of this change is to clean up some of the code surrounding
HLSL using CXXThisExpr as a non-pointer l-value. This change cleans up
a bunch of assumptions and inconsistencies around how the type of
`this` is handled through the AST and code generation.
This change is be mostly NFC for HLSL, and completely NFC for other
language modes.
This change introduces a new member to query for the this object's type
and seeks to clarify the normal usages of the this type.
With the introudction of HLSL to clang, CXXThisExpr may now be an
l-value and behave like a reference type rather than C++'s normal
method of it being an r-value of pointer type.
With this change there are now three ways in which a caller might need
to query the type of `this`:
* The type of the `CXXThisExpr`
* The type of the object `this` referrs to
* The type of the implicit (or explicit) `this` argument
This change codifies those three ways you may need to query
respectively as:
* CXXMethodDecl::getThisType()
* CXXMethodDecl::getThisObjectType()
* CXXMethodDecl::getThisArgType()
This change then revisits all uses of `getThisType()`, and in cases
where the only use was to resolve the pointee type, it replaces the
call with `getThisObjectType()`. In other cases it evaluates whether
the desired returned type is the type of the `this` expr, or the type
of the `this` function argument. The `this` expr type is used for
creating additional expr AST nodes and for member lookup, while the
argument type is used mostly for code generation.
Additionally some cases that used `getThisType` in simple queries could
be substituted for `getThisObjectType`. Since `getThisType` is
implemented in terms of `getThisObjectType` calling the later should be
more efficient if the former isn't needed.
Reviewed By: aaron.ballman, bogner
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D159247
In dataflow analysis, SAT solver: simplify formula during CNF construction and short-cut
solving when the formula has been recognized as contradictory.
Reviewed By: sammccall
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D158407
This makes `ExprToVal` dumping consistent with `LocToVal` dumping.
Reviewed By: ymandel, xazax.hun
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D159274
Instead, map prvalue expressions directly to values in a newly introduced map `Environment::ExprToVal`.
This change introduces an additional member variable in `Environment` but is an overall win:
- It is more conceptually correctly, since prvalues don't have storage
locations.
- It eliminates complexity from
`Environment::setValue(const Expr &E, Value &Val)`.
- It reduces the amount of data stored in `Environment`: A prvalue now has a
single entry in `ExprToVal` instead of one in `ExprToLoc` and one in
`LocToVal`.
- Not allocating `StorageLocation`s for prvalues additionally reduces memory
usage.
This patch is the last step in the migration to strict handling of value categories (see https://discourse.llvm.org/t/70086 for details). The changes here are almost entirely internal to `Environment`.
The only externally observable change is that when associating a `RecordValue` with the location returned by `Environment::getResultObjectLocation()` for a given expression, callers additionally need to associate the `RecordValue` with the expression themselves.
Reviewed By: xazax.hun
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D158977
Instead, inline them into the `getStableStorageLocation()` overloads, which is the only place they were called from (and should be called from).
`getStorageLocation()` / `setStorageLocation()` were confusing because neither their name nor their documentation made reference to the fact that the storage location is stable.
It didn't make sense to keep these as private member functions either. The code for the two `getStableStorageLocation()` overloads has become only marginally more complex by inlining these functions, and the `Expr` version is actually more efficient because we only call `ignoreCFGOmittedNodes()` once instead of twice.
Reviewed By: ymandel, xazax.hun
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D158981
Adds support for recognizing range-for loops in the main algorithm for computing
the model fixpoint.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D158848